EVOLVE CYCLO MNP Eye Drops 5ml
Iminoral Oral Solution 50ml
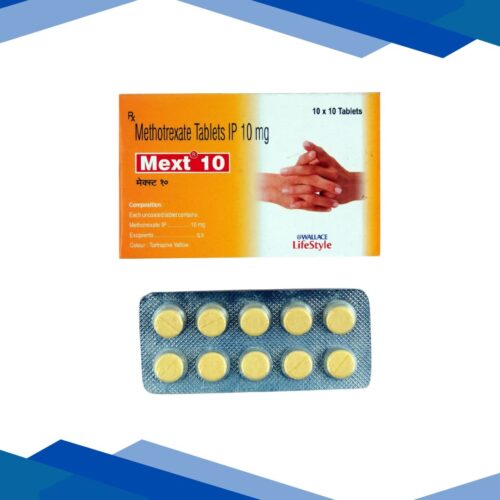
SPRINTAS 50mg Capsule 5’s
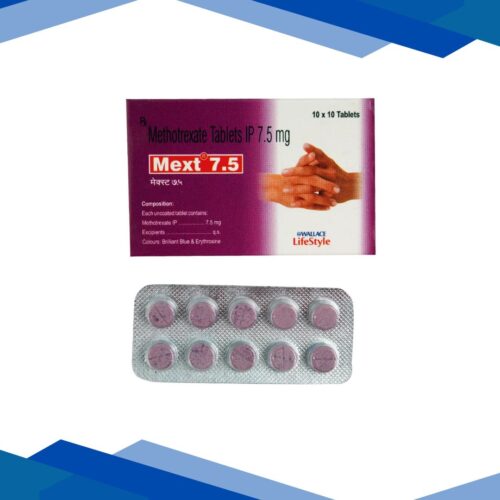
PASILOW 100mg Capsule 5’s
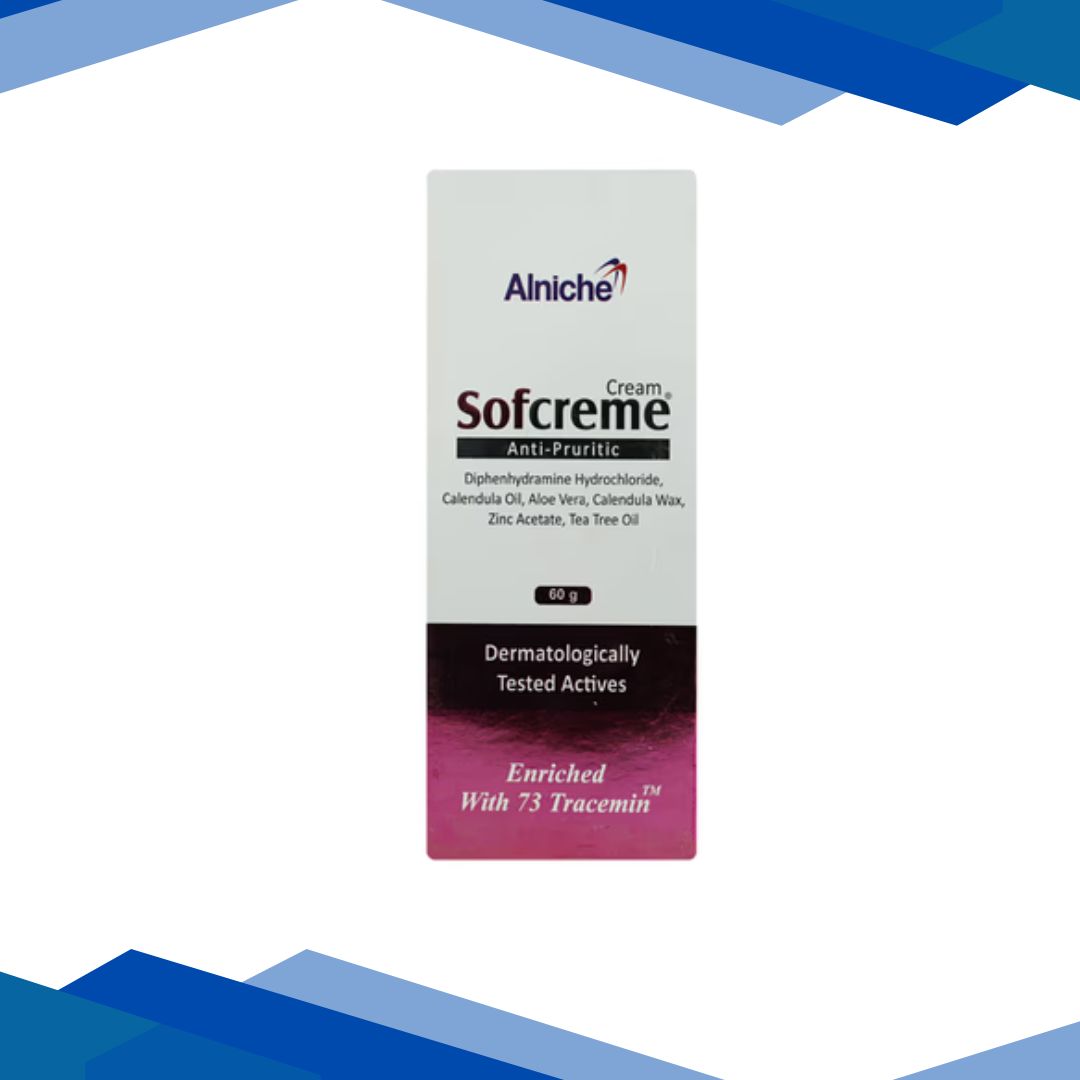
SOFCREME Cream 60gm
No Prescription yet? Don’t worry! Click Here to Get Online Consultation
Why Prescription is Required?
✅ Providing Right Medicines
Prescriptions are complex documents. We proofread and recheck at various steps to provide you the right medication in the correct form and dose.
⚖️ Helps Comply with the Law
Most medicines cannot be sold without a valid prescription, as per the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940 and Rules, 1945.
Book Appointment with Doctor
SOFCREME Cream 60 gm is a topical anti‑pruritic and skin‑soothing cream used to relieve itching, irritation, dryness and discomfort associated with minor skin conditions such as insect bites, rashes, sun exposure, or other mild irritations while also hydrating and nourishing the skin. For more details kindly click on Medicine Salts below:
Aloe Vera
ALOE VERA
Overview:
Aloe Vera, also known as Aloe barbadensis, is a succulent plant widely recognized for its soothing, healing, and moisturizing properties. It’s been used for centuries in traditional medicine and skincare around the world often found in gels, juices, creams, and dietary supplements.
Classification: Succulent plant
Uses:
Topical (applied on the skin):
Soothing sunburns
Healing minor cuts, wounds, and burns
Reducing skin irritation or itchiness (eczema, psoriasis)
Moisturizing dry skin
Oral (taken internally, in juice or supplement form):
Supporting digestive health
Relieving constipation (mainly from aloe latex—used cautiously)
Promoting gut healing (in cases of acid reflux or ulcers)
Supporting detoxification
How It Works:
Aloe Vera works through its rich mix of bioactive compounds, including:
Polysaccharides – Help with skin repair and hydration
Aloin and Emodin – Found in the latex; can act as strong laxatives
Vitamins (A, C, E, B12) – Support healing and fight oxidative stress
Enzymes & Amino Acids – Aid in anti-inflammatory effects and skin repair
Anti-bacterial & Anti-fungal agents – Help prevent infection in wounds
Its cooling effect makes it particularly helpful for calming inflamed or sun-damaged skin.
Dosage: As prescribed by your doctor.
Side effects:
While generally safe when used properly, Aloe Vera can sometimes cause:
Topically: Skin irritation or allergic reactions in sensitive individuals
Dryness if overused
Orally: Stomach cramps, diarrhea, or electrolyte imbalance (especially from aloe latex)
Lowered blood sugar (a concern for diabetics)
Precautions:
Do a patch test before using on skin to avoid allergic reactions
Avoid aloe latex if pregnant, breastfeeding, or dealing with intestinal problems
Consult a doctor if you’re on medications (especially for diabetes, heart, or kidneys)
Use food-grade products only if ingesting aloe juice or supplements
Disclaimer:
This content is for informational purposes only. Always consult a healthcare provider for medical advice and proper dosage
Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride
DIPHENHYDRAMINE
Overview
Diphenhydramine is a commonly used medicine to treat allergic reactions, cold symptoms, and itching. It also acts as a sleep aid and helps relieve motion sickness or nausea. It’s available in various forms, including tablets, syrups, creams, and injections.
Classification
Antihistamine
Uses
Eases allergy symptoms like sneezing, runny nose, watery eyes, and hives
Soothes skin irritation and itching due to insect bites, rashes, or eczema
Helps with insomnia (difficulty sleeping)
Used to prevent and manage motion sickness
Relieves cough and cold symptoms when combined with other ingredients
Sometimes used for mild anxiety or restlessness
How It Works
Diphenhydramine works by blocking histamine, a natural substance your body releases during allergic reactions. It also affects certain brain chemicals to cause drowsiness, which helps with sleep and reduces motion-related nausea or dizziness.
Dosage
As prescribed by your doctor.
Side effects
Common effects may include:
Drowsiness or sleepiness
Dry mouth, nose, or throat
Dizziness or blurred vision
Upset stomach or constipation
Feeling groggy or uncoordinated, especially in older adults
Precautions
Can cause drowsiness—avoid driving or operating heavy machinery after taking
Should be used cautiously in older adults, as it may cause confusion or falls
Let your doctor know if you have asthma, glaucoma, high blood pressure, or an enlarged prostate
Avoid alcohol and other sedatives while using this medicine
Not usually recommended for children under 6 without medical advice
If pregnant or breastfeeding, consult your doctor before using
Disclaimer
This content is for informational purposes only. Always consult a healthcare provider for medical advice and proper dosage