ZUKANORM M 500 Tablet 20’s
VILDAPRIDE D 100/10 Tablet 10’s
INTAGLIP M SR 500 Tablet 10’s
REMO MV 1000 Tablet 10’s
VILDANA 50mg Tablet 10’s
NUHIST TABLET 10’S
No Prescription yet? Don’t worry! Click Here to Get Online Consultation
Why Prescription is Required?
✅ Providing Right Medicines
Prescriptions are complex documents. We proofread and recheck at various steps to provide you the right medication in the correct form and dose.
⚖️ Helps Comply with the Law
Most medicines cannot be sold without a valid prescription, as per the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940 and Rules, 1945.
Book Appointment with Doctor
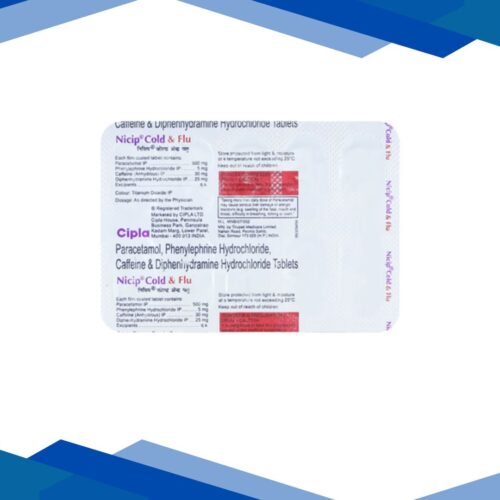
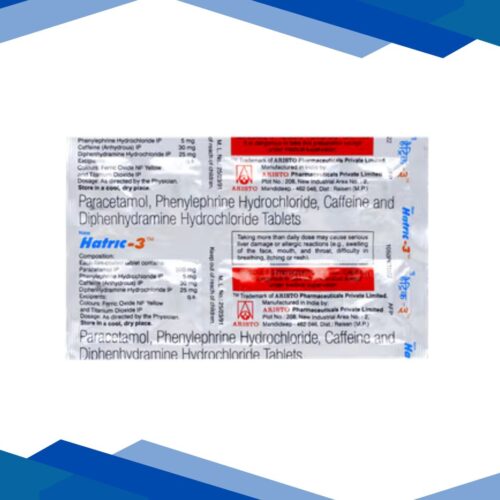
NUHIST is a combination of Caffeine, Diphenhydramine, Paracetamol, and Phenylephrine which belongs to the group of medicines called CNS Stimulants, Antihistamines, Analgesics-Antipyretics, and Nasal Decongestants respectively. It is used to relieve flu and cold symptoms, headache, body ache, extreme weakness, watery eyes, fever, cough, sore throat, sneezing, runny, and congested nose.
Caffeine
CAFFEINE
Overview:
Caffeine is a natural substance that helps you feel less tired and more awake. You’ll find it in things like coffee, tea, cola, energy drinks, and even in some medications.
Classification: Central nervous system stimulants
Uses:
Fights sleepiness and helps keep you focused
Can help you stay mentally sharp during the day
Often added to pain relievers to make them work better (like in migraine treatment)
Sometimes used in newborns (especially premature babies) to help with breathing problems
How it works:
Caffeine helps you stay awake and focused by blocking a brain chemical called adenosine, which normally makes you feel drowsy.
By stopping adenosine, caffeine keeps your brain more active, helping you feel energized, alert, and a bit more awake. It can also slightly increase your heart rate and make you feel more awake physically and mentally.
Dosage: As prescribed by your doctor.
Side effects:
Having too much caffeine might cause:
Restlessness or shaky hands
Trouble falling asleep
Rapid heartbeat or a racing pulse
Stomach discomfort or acidity
Mild headaches, especially if you suddenly stop using it
Frequent urination
Feeling uneasy or anxious
Precautions:
Don’t have too much: Taking in large amounts of caffeine can make you feel nervous, interfere with sleep, or cause a fast heartbeat. It’s best to keep it moderate—about 1 to 3 cups of tea or coffee a day is usually safe.
If you’re sensitive, go slow: Some people react strongly to even small doses of caffeine, causing shakiness, headaches, or discomfort.
Avoid it before bedtime: Since caffeine keeps you alert, having it too late in the day (especially after the afternoon) can make it hard to fall asleep.
Pregnant or breastfeeding? Talk to your doctor. Too much caffeine might affect your baby, so it’s safer to limit your intake.
If you have heart issues, anxiety, or high blood pressure: Be careful—caffeine can sometimes worsen these problems.
Check food and medicine labels: Caffeine isn’t only in coffee—it’s also found in soft drinks, energy drinks, chocolate, and some pills like pain relievers or slimming products.
Disclaimer:
This content is for informational purposes only. Always consult a healthcare provider for medical advice and proper dosage
Diphenhydramine Hydrochloride
DIPHENHYDRAMINE
Overview
Diphenhydramine is a commonly used medicine to treat allergic reactions, cold symptoms, and itching. It also acts as a sleep aid and helps relieve motion sickness or nausea. It’s available in various forms, including tablets, syrups, creams, and injections.
Classification
Antihistamine
Uses
Eases allergy symptoms like sneezing, runny nose, watery eyes, and hives
Soothes skin irritation and itching due to insect bites, rashes, or eczema
Helps with insomnia (difficulty sleeping)
Used to prevent and manage motion sickness
Relieves cough and cold symptoms when combined with other ingredients
Sometimes used for mild anxiety or restlessness
How It Works
Diphenhydramine works by blocking histamine, a natural substance your body releases during allergic reactions. It also affects certain brain chemicals to cause drowsiness, which helps with sleep and reduces motion-related nausea or dizziness.
Dosage
As prescribed by your doctor.
Side effects
Common effects may include:
Drowsiness or sleepiness
Dry mouth, nose, or throat
Dizziness or blurred vision
Upset stomach or constipation
Feeling groggy or uncoordinated, especially in older adults
Precautions
Can cause drowsiness—avoid driving or operating heavy machinery after taking
Should be used cautiously in older adults, as it may cause confusion or falls
Let your doctor know if you have asthma, glaucoma, high blood pressure, or an enlarged prostate
Avoid alcohol and other sedatives while using this medicine
Not usually recommended for children under 6 without medical advice
If pregnant or breastfeeding, consult your doctor before using
Disclaimer
This content is for informational purposes only. Always consult a healthcare provider for medical advice and proper dosage
Paracetamol
PARACETAMOL
Overview
Paracetamol is a commonly used medication that helps relieve mild to moderate pain and reduce fever. It’s often used for:
Headaches
Toothaches
Muscle and back pain
Menstrual cramps
Cold and flu symptoms
It’s available over-the-counter and is considered safe when used as directed.
Classification
Analgesic and antipyretic agent
Uses
Paracetamol is used for pain relief and fever. It is used to relieve pain in conditions like headache, muscle pain, or dental pain.
How it works
When you produce a fever, your body’s internal thermostat — found in the hypothalamus portion of the brain — is raised to a higher temperature. This new set point is usually induced by pyrogens (substances made during infections) that tell the body to produce more heat as a form of immune defense.
Due to its effects in the brain, paracetamol reduces the production of reactive prostaglandins. Prostaglandins are disease-fighting chemicals released during infection that in turn, raise the body’s temperature set point. By decreasing prostaglandin levels, paracetamol enables the hypothalamus’ temperature control centre to bring the body’s temperature back down to normal, allowing the body to cool down and the fever to subside
Dosage
As directed by the physician
Precautions
Most people can take paracetamol safely, including:
pregnant women
breastfeeding women
children over 2 months of age – lower doses are recommended for young children
always get advice before taking paracetamol if you:
have liver or kidney problems
have problems with alcohol, like long-term alcohol misuse
are very underweight
are taking other medications
Don’t take paracetamol if you’ve had an allergic reaction to it in the past
Side effects
common side effects of paracetamol.
Nausea
Swelling
Vomiting
Pain
Tenderness in the upper abdomen
Sweating
Loss of appetite
Stomach cramps
Diarrhea
Major side effects are as follows:
Dark-colored urine
High fever
Lower backache
Skin having red spots
Rashes
Inflammation
Itching
Sore throat
Ulcers
Breathlessness
Yellowish eyes
Disclaimer
This content is for informational purposes only. Always consult a healthcare provider for medical advice and proper dosage.
Phenylephrine
PHENYLEPHRINE
Overview
Phenylephrine is a medicine often used to relieve a stuffy or blocked nose. It works by shrinking swollen blood vessels in your nasal passages, helping you breathe more easily. You might find it in many cold, flu, or allergy medications.
Classification
Decongestants
Uses
Relieves nasal congestion due to colds, allergies, or sinus infections
Sometimes used to increase low blood pressure during surgery or in critical care
May be found in eye drops to dilate pupils during eye exams
How It Works
Phenylephrine works by narrowing the blood vessels in the nose. This reduces swelling and opens up your airways. When taken for blood pressure support, it tightens blood vessels throughout the body, which helps raise blood pressure.
Dosage
As prescribed by your doctor.
Side effects
Some common or possible side effects may include:
Headache
Dizziness
Nervousness or restlessness
Trouble sleeping (insomnia)
Increased heart rate or blood pressure
In rare cases, serious side effects like irregular heartbeat or chest pain can occur. Always report unusual symptoms to your doctor.
Precautions
Avoid it if you have high blood pressure, heart disease, thyroid problems, or glaucoma, unless your doctor says it’s safe.
Do not use more than the recommended dose – overuse can increase side effects.
Tell your doctor if you’re pregnant or breastfeeding before using.
If taken with other medications (especially for depression or blood pressure), it could interact negatively.
Not recommended for young children without medical advice.
Disclaimer
This content is for informational purposes only. Always consult a healthcare provider for medical advice and proper dosage