OMEGA 3
Overview
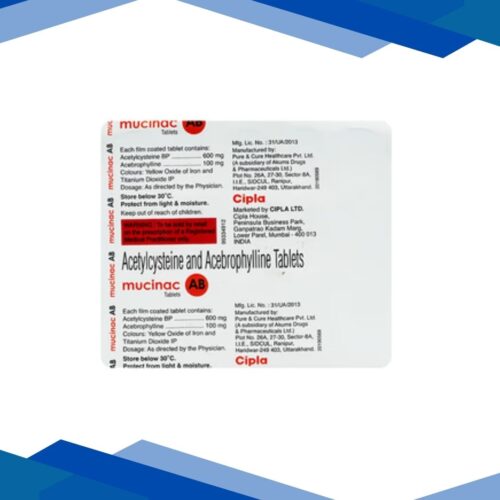
Omega-3 is a type of healthy fat that is very important for your heart, brain, eyes, and overall health. Since the body can’t make it on its own, you need to get it from food (like fish) or supplements (like capsules or syrups).
Classification
Omega-3 belongs to the group of essential fatty acids. The main types are:
EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid)
DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid)
ALA (Alpha-linolenic Acid)
EPA and DHA are mostly found in fish oil, while ALA comes from plant sources like flaxseeds.
Uses
Omega-3 is used for:
Keeping the heart healthy
Lowering bad cholesterol and triglycerides
Improving brain health and memory
Reducing joint pain and stiffness (like in arthritis)
Supporting eye health
Helping during pregnancy for baby’s brain development
How It Works
Omega-3 works by:
Reducing inflammation in the body
Keeping blood vessels flexible and clear
Lowering fats in the blood
Supporting brain cells and eye function
It helps keep your heart, brain, and body working smoothly.
Dosage
As prescribed by your doctor.
Side effects
Generally safe, but some people may notice:
Fishy aftertaste or burps
Stomach upset
Loose stools (mild diarrhea)
Nausea
Very high doses may slightly increase bleeding risk or cause low blood pressure.
Precautions
Take it with food to avoid stomach issues.
Tell your doctor if you’re on blood thinners (like aspirin or warfarin).
Check with a doctor before using during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
If you have seafood allergy, use plant-based Omega-3 sources.
Store supplements in a cool, dry place to avoid spoilage.
Disclaimer
This content is for informational purposes only. Always consult a healthcare provider for medical advice and proper dosage