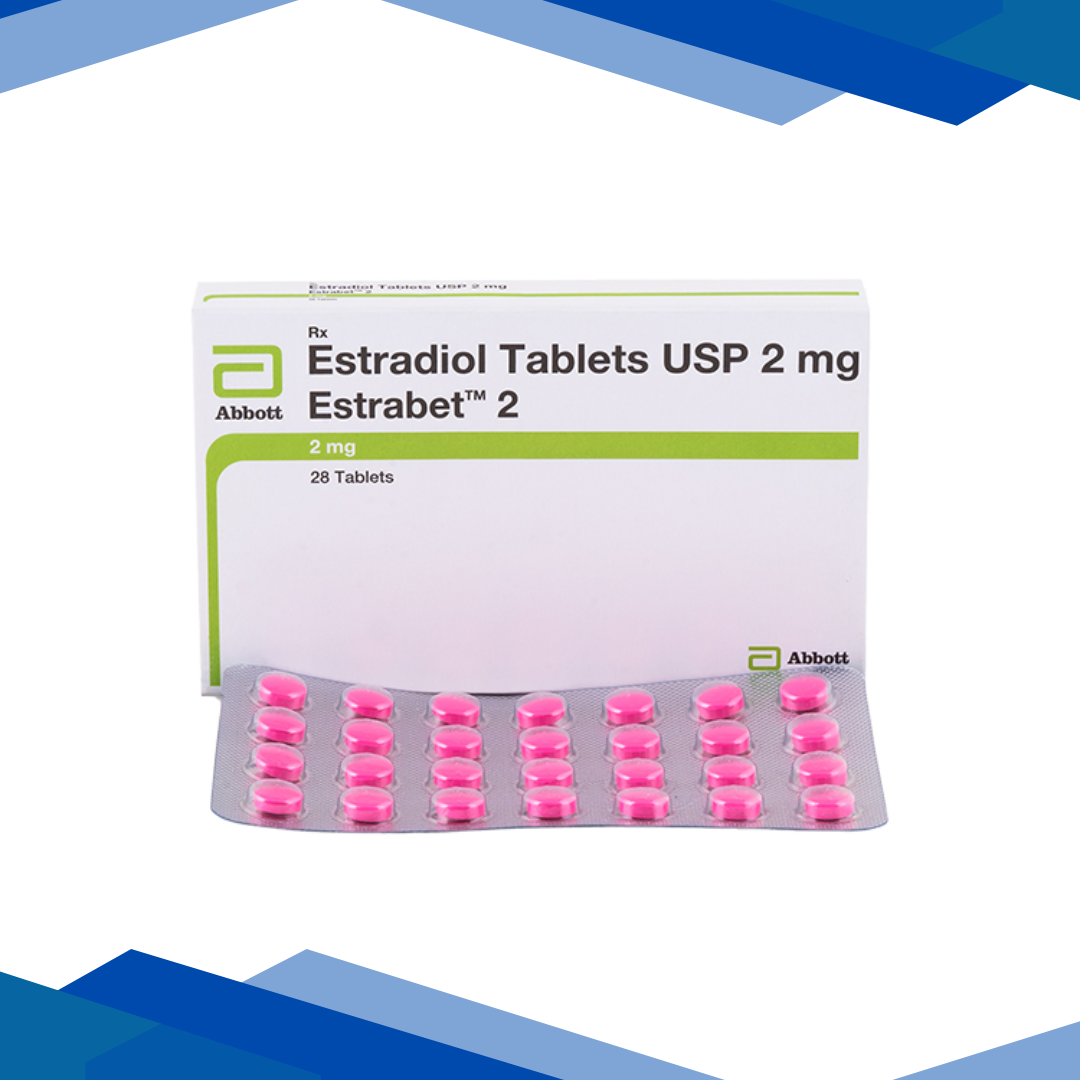
Estradiol
ESTRADIOL
Overview:
Estradiol is a type of estrogen, the main female hormone produced by the ovaries. It helps regulate the menstrual cycle, support reproductive health, and keep bones and the heart healthy.It is often prescribed to manage menopause-related issues, including hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness, and to protect bone health.
Classification: Estrogen hormone
Uses:
Estradiol is used to relieve symptoms of menopause, such as hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness. It also helps prevent bone loss and reduce the risk of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Additionally, it supports hormonal balance and can be part of therapy for estrogen replacement, including for women who have had their ovaries removed or transgender individuals.
How it works:
Estradiol works by attaching to estrogen receptors in tissues such as the uterus, bones, and brain, and then turns on genes that regulate their growth, development, and function. This helps regulate the menstrual cycle, maintain bone density, support heart health, and relieve menopause symptoms such as hot flashes and vaginal dryness.
Dosage: As prescribed by your doctor.
Side Effects:
- Nausea or vomiting
- Breast tenderness or swelling
- Headache
- Mood changes
- Bloating or water retention
- Spotting or breakthrough bleeding
Precautions:
Estradiol should be used carefully in people with a history of breast cancer, blood clots, liver problems, or heart disease. Always tell your doctor about any other medications you are taking, especially blood thinners or hormone-related drugs. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should only use it if advised by a healthcare professional. While taking estradiol, watch for unusual bleeding, severe headaches, swelling, or shortness of breath, and avoid smoking, as it can increase the risk of blood clots.
Disclaimer:This content is for informational purposes only. Always consult a healthcare provider for medical advice and proper dosage.