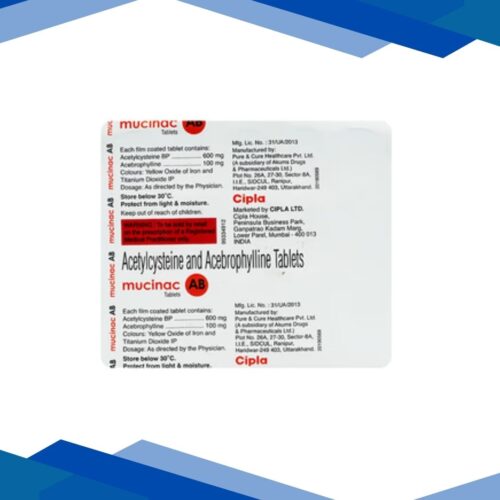
MUCINAC AB Tablet 15’s
Megatin Dc
No Prescription yet? Don’t worry! Click Here to Get Online Consultation
Why Prescription is Required?
✅ Providing Right Medicines
Prescriptions are complex documents. We proofread and recheck at various steps to provide you the right medication in the correct form and dose.
⚖️ Helps Comply with the Law
Most medicines cannot be sold without a valid prescription, as per the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940 and Rules, 1945.
Book Appointment with Doctor
Megatin Dc Capsule belongs to the group of ‘penicillin antibiotics’ used to treat a wide range of bacterial infections. It is a ‘broad-spectrum antibiotic’ that treats various bacterial infections of the ear, nose, throat, bones, lungs, and post-operative wound infections. For more details kindly click on Medicine Salts below:
Amoxycillin
AMOXYCILLIN
Overview:
Amoxycillin is an antibiotic used for stopping growth of bacterial infections.
Classification: Penicillin group antibiotic
Mechanism of action: Amoxycillin inhibits the formation of cell wall by bacteria and thereby killing them.
Uses:
– Skin infections
– Dental infections
– Urinary tract infections
– Respiratory tract infections
– Ear, nose, and throat infections
Dosage:
As per prescription of your doctor.
Side Effects:
Common side effects include:
– Loose stools
– Skin rash
– Nausea
– Allergic reactions (rare but serious)
Precautions:
– Inform your doctor about any allergies to penicillin.
– Use with caution in patients with kidney problems.
– Not effective against viral infections (e.g., flu or cold).
Disclaimer:
This information is for educational purposes only. Always consult a doctor or pharmacist before using any medication.
Dicoloxacillin
DICLOXACILLIN
Overview:
Dicloxacillin is an antibiotic that helps in fighting a few bacterial diseases and most of all staphylococcus bacterium. It works by making the cell wall in the bacteria weak and this inhibits growth and multiplication of bacteria. Usually, it is given to physicians as therapy for skin infection, ear infection, bone infection, or pulmonary infection by these bacteria. It exists in tablet form and in something called an injection, which is taken as prescribed. The entire course will help to clear up the infection and the bacteria will not be resistant.
Classification: Penicillin (β-lactam) antibiotic
Uses:
Dicloxacillin is applied to bacterial infections which are caused by some staph bacteria. It may be used to treat skin infections (boils, cellulitis), lung infections (pneumonia), ear infections, and infections of the bones or joints. It prevents the spread of infection by destroying the bacteria and makes your body better. It can be taken in the form of tablets or injections and it is necessary to take it as your doctor has suggested.
How it works:
Dicloxacillin is a 2-lactam penicillin antibiotic, which inhibits the synthesis of the cell wall of bacterial cells by binding itself to penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) on the bacterial cell wall, which prevents the cross-linking of peptidoglycan chains, which are needed to make the bacterial cell wall strong and rigid. This destabilizes the bacterial cell wall and causes cell lysis and death of bacteria. It is also bactericidal, that is, it actively kills the susceptible bacteria; it is therefore effective against the infections that are sensitive to penicillin in the Staphylococcus.
Dosage: As prescribed by your doctor.
Side Effects:
- Nausea or vomiting
- Stomach upset or abdominal pain
- Diarrhea
- Skin rash or itching (allergic reaction)
- Swelling of lips, tongue, or face (rare but serious allergy)
- Difficulty breathing (severe allergic reaction)
- Yellowing of skin or eyes (rare liver problem)
Precautions:
- Let your doctor know if you have any allergies to penicillin or similar antibiotics.
- Take the medicine exactly as prescribed and complete the full course.
- Use with caution in people with liver or kidney problems.
- Let your healthcare provider know all the medications you take so they don’t interfere with each other.
- For best results, swallow the capsules on an empty stomach, either before eating or a while after.
- Tell your doctor right away if you notice a rash, swelling, or trouble breathing.
- If diarrhea becomes severe or persistent, contact your doctor (possible sign of C. difficile infection).
Disclaimer:This content is for informational purposes only. Always consult a healthcare provider for medical advice and proper dosage.