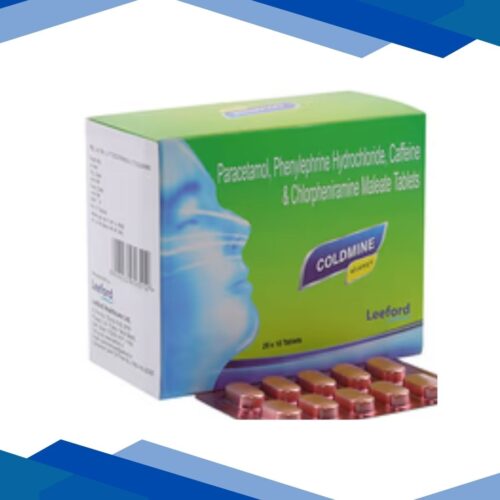
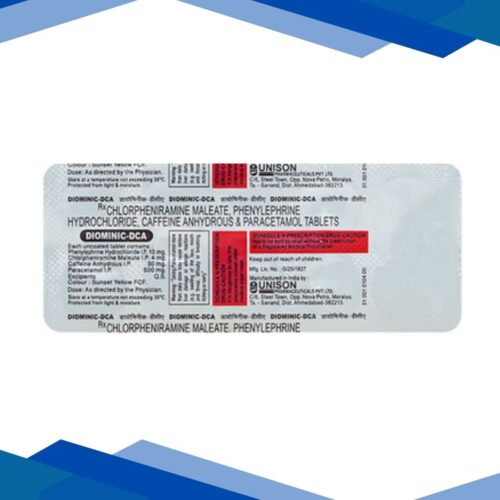
4 QUIN D Eye Drops 5ml
DECAMOX M Eye Drops 5ml
Mahaflox D Eye Drops 5ml
CEFLOX DEE OPTIC Eye/Ear Drops 10ml
Apdrops DM Eye Drops 5ml
Brillare Caffiene Shampoo
Brillare Caffeine Shampoo is a hair‑fall control shampoo that helps strengthen weak strands, reduce breakage, and support healthier hair growth. For more details kindly click on Medicine Salts below :
Aloe Vera
ALOE VERA
Overview:
Aloe Vera, also known as Aloe barbadensis, is a succulent plant widely recognized for its soothing, healing, and moisturizing properties. It’s been used for centuries in traditional medicine and skincare around the world often found in gels, juices, creams, and dietary supplements.
Classification: Succulent plant
Uses:
Topical (applied on the skin):
Soothing sunburns
Healing minor cuts, wounds, and burns
Reducing skin irritation or itchiness (eczema, psoriasis)
Moisturizing dry skin
Oral (taken internally, in juice or supplement form):
Supporting digestive health
Relieving constipation (mainly from aloe latex—used cautiously)
Promoting gut healing (in cases of acid reflux or ulcers)
Supporting detoxification
How It Works:
Aloe Vera works through its rich mix of bioactive compounds, including:
Polysaccharides – Help with skin repair and hydration
Aloin and Emodin – Found in the latex; can act as strong laxatives
Vitamins (A, C, E, B12) – Support healing and fight oxidative stress
Enzymes & Amino Acids – Aid in anti-inflammatory effects and skin repair
Anti-bacterial & Anti-fungal agents – Help prevent infection in wounds
Its cooling effect makes it particularly helpful for calming inflamed or sun-damaged skin.
Dosage: As prescribed by your doctor.
Side effects:
While generally safe when used properly, Aloe Vera can sometimes cause:
Topically: Skin irritation or allergic reactions in sensitive individuals
Dryness if overused
Orally: Stomach cramps, diarrhea, or electrolyte imbalance (especially from aloe latex)
Lowered blood sugar (a concern for diabetics)
Precautions:
Do a patch test before using on skin to avoid allergic reactions
Avoid aloe latex if pregnant, breastfeeding, or dealing with intestinal problems
Consult a doctor if you’re on medications (especially for diabetes, heart, or kidneys)
Use food-grade products only if ingesting aloe juice or supplements
Disclaimer:
This content is for informational purposes only. Always consult a healthcare provider for medical advice and proper dosage
Caffeine
CAFFEINE
Overview:
Caffeine is a natural substance that helps you feel less tired and more awake. You’ll find it in things like coffee, tea, cola, energy drinks, and even in some medications.
Classification: Central nervous system stimulants
Uses:
Fights sleepiness and helps keep you focused
Can help you stay mentally sharp during the day
Often added to pain relievers to make them work better (like in migraine treatment)
Sometimes used in newborns (especially premature babies) to help with breathing problems
How it works:
Caffeine helps you stay awake and focused by blocking a brain chemical called adenosine, which normally makes you feel drowsy.
By stopping adenosine, caffeine keeps your brain more active, helping you feel energized, alert, and a bit more awake. It can also slightly increase your heart rate and make you feel more awake physically and mentally.
Dosage: As prescribed by your doctor.
Side effects:
Having too much caffeine might cause:
Restlessness or shaky hands
Trouble falling asleep
Rapid heartbeat or a racing pulse
Stomach discomfort or acidity
Mild headaches, especially if you suddenly stop using it
Frequent urination
Feeling uneasy or anxious
Precautions:
Don’t have too much: Taking in large amounts of caffeine can make you feel nervous, interfere with sleep, or cause a fast heartbeat. It’s best to keep it moderate—about 1 to 3 cups of tea or coffee a day is usually safe.
If you’re sensitive, go slow: Some people react strongly to even small doses of caffeine, causing shakiness, headaches, or discomfort.
Avoid it before bedtime: Since caffeine keeps you alert, having it too late in the day (especially after the afternoon) can make it hard to fall asleep.
Pregnant or breastfeeding? Talk to your doctor. Too much caffeine might affect your baby, so it’s safer to limit your intake.
If you have heart issues, anxiety, or high blood pressure: Be careful—caffeine can sometimes worsen these problems.
Check food and medicine labels: Caffeine isn’t only in coffee—it’s also found in soft drinks, energy drinks, chocolate, and some pills like pain relievers or slimming products.
Disclaimer:
This content is for informational purposes only. Always consult a healthcare provider for medical advice and proper dosage