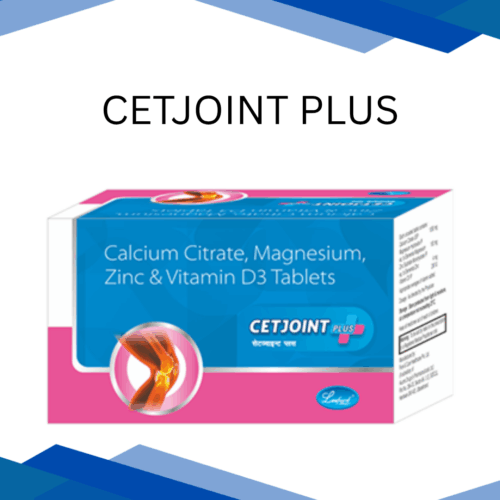
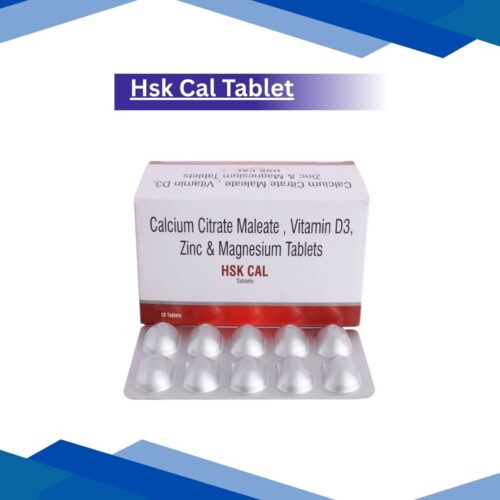
Vitamin B6
VITAMIN B6
Overview
Vitamin B6 is an essential nutrient that your body needs to stay healthy. It plays a big role in keeping your nerves, brain, and blood cells working properly. Since your body can’t make it on its own, you get it from food or supplements
Classification
Vitamin B6 is a water-soluble vitamin, part of the B-complex family. This means it dissolves in water and doesn’t stay stored in the body for long — so you need to take it regularly through diet or supplements.
Uses
Vitamin B6 is used for:
Boosting brain function and mood
Supporting healthy nerves
Forming red blood cells
Helping the body break down proteins and carbs
Relieving nausea during pregnancy
Improving PMS symptoms
Preventing or treating vitamin B6 deficiency
How It Works
Vitamin B6 helps the body:
Make neurotransmitters – chemicals that send messages in the brain
Produce hemoglobin – the part of red blood cells that carries oxygen
Break down food into energy
Keep the immune system strong
In short, it helps your brain, nerves, and metabolism stay in balance.
Dosage
As prescribed by your doctor.
Side effects
Usually safe when taken in normal amounts. But in large doses or long-term use:
Numbness or tingling in hands and feet
Nausea or stomach pain
Sensitivity to sunlight
Tiredness or headache
Nerve damage (very high doses over time)
Precautions
Don’t take high doses for a long time without a doctor’s advice.
Talk to your doctor if you have nerve problems, kidney disease, or are on other medications.
Safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding in recommended doses, but avoid overdosing.
Always follow the label or doctor’s instructions for the correct dosage.
Disclaimer
This content is for informational purposes only. Always consult a healthcare provider for medical advice and proper dosage
ZINC
ZINC
Overview:
zinc is an essential nutrient found in a variety of plant and animal foods, along with supplements. It plays a key role in skin health, immune function, and cell growth and may protect against acne, inflammation, and other conditions.
Classification:
Antioxidant
Uses:
Supports the heart and nervous system
Has antioxidant effects
Supports the immune system
Helps in the formation of red blood cells
How It Works:
Cofactor Role:
Zinc acts as a cofactor for thousands of enzymes and proteins, which are essential for various metabolic processes.
Immune Function:
Zinc is crucial for the proper functioning of the immune system, including the production of immune cells like T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells.
Antiviral Effects:
Zinc may help reduce the severity of colds by inhibiting rhinovirus replication and suppressing nasal inflammation.
Wound Healing:
Zinc is involved in collagen synthesis and other processes that contribute to wound repair.
DNA Synthesis:
Zinc is essential for DNA replication and RNA transcription, which are fundamental processes for cell growth and function.
Dosage:
As prescribed by your doctor.
Side Effects:
Diarrhea.
Dizziness.
Headache.
Nausea.
Upset stomach.
Vomiting.
Precautions:
Read the label carefully before use
Store in a cool and dry place away from direct sunlight
Keep out of reach of children
Use under medical supervision
Do not exceed the recommended dosage
Pregnant or nursing mothers, children, and people with medical conditions must consult a healthcare professional before taking this supplement
Disclaimer
This content is for informational purposes only. Always consult a healthcare provider for medical advice and proper dosage.